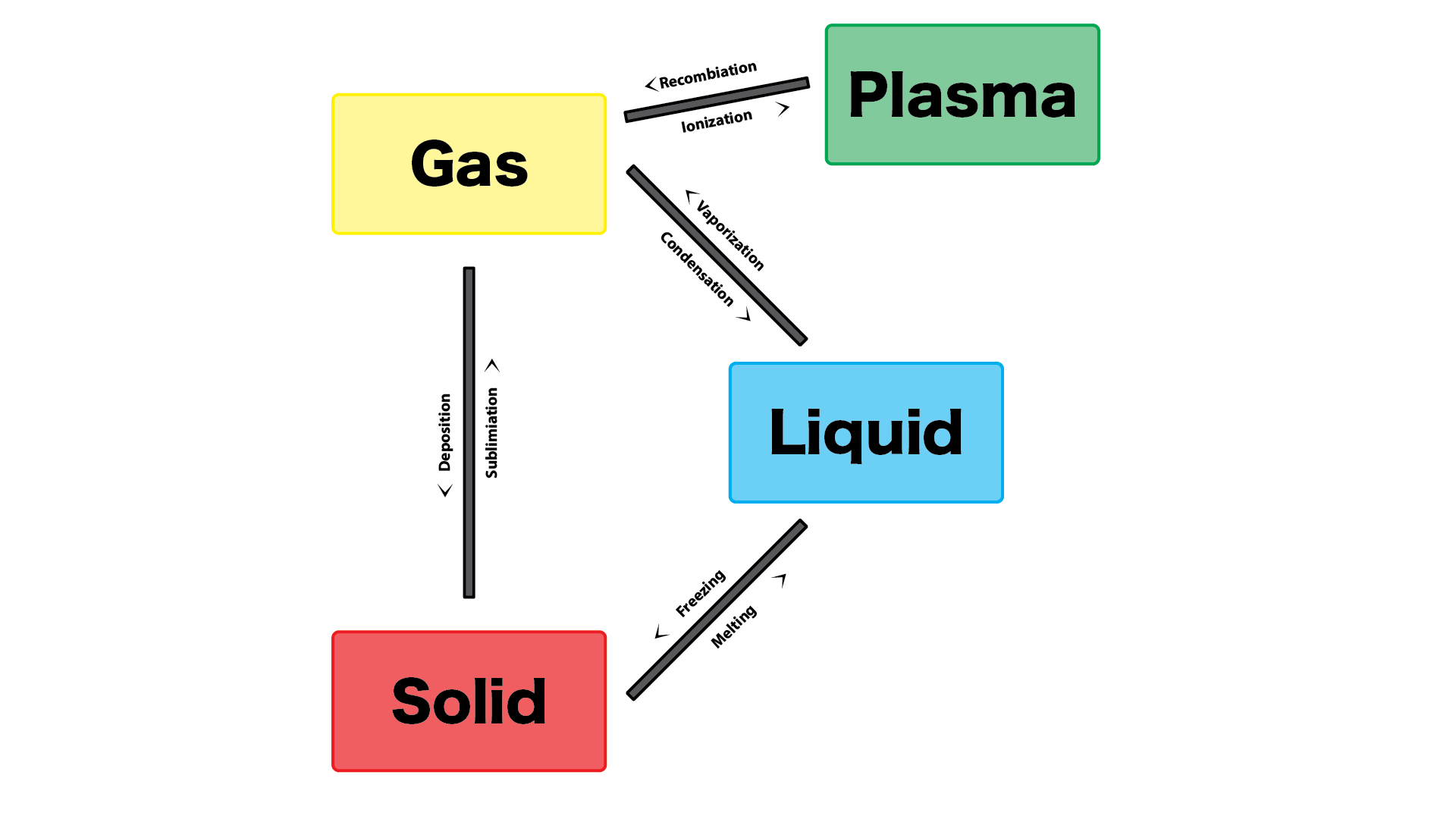
Melting is the phase change where a solid turns into a liquid when heat is added. As the temperature increases, the molecules within the solid gain enough energy to overcome the forces that hold them together, allowing them to move more freely. This transition occurs at the substance’s melting point, where the solid's structure begins to break down into a liquid. An example of this is when ice melts into water as it warms above 0°C.
Freezing is the reverse of melting, where a liquid turns into a solid when it loses heat. As the liquid cools, its molecules lose energy and slow down, eventually becoming arranged in a fixed, orderly structure. This process happens at the freezing point of the substance, which is the same temperature as the melting point but in the opposite direction. For example, water freezes into ice at 0°C when the temperature drops.
Evaporation is the phase change from liquid to gas, typically occurring at the surface of the liquid when heat is applied. Molecules at the surface of the liquid gain enough energy to break free from the liquid and enter the air as vapor. Evaporation happens at any temperature, although it is faster at higher temperatures. A common example of evaporation is when water in a puddle slowly disappears on a warm day.
Condensation is the phase change where a gas turns into a liquid as it loses heat. When the temperature of a gas decreases, its molecules slow down and come closer together, forming a liquid. This is commonly observed when water vapor in the air cools down, forming water droplets on a cold glass or mirror. It is the process responsible for dew formation and the fogging up of windows.
Sublimation occurs when a solid turns directly into a gas without passing through the liquid state. This happens when the molecules in the solid gain enough energy to escape directly into the gas phase. An example of sublimation is the transition of dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) into carbon dioxide gas at room temperature, bypassing the liquid phase entirely.
Deposition is the opposite of sublimation, where a gas turns directly into a solid without becoming a liquid. This occurs when gas molecules lose enough energy that they slow down and bond together to form a solid. An example of deposition is the formation of frost on a cold surface, where water vapor in the air directly forms solid ice crystals without first becoming liquid water.